LPA1 Receptor Antibodies
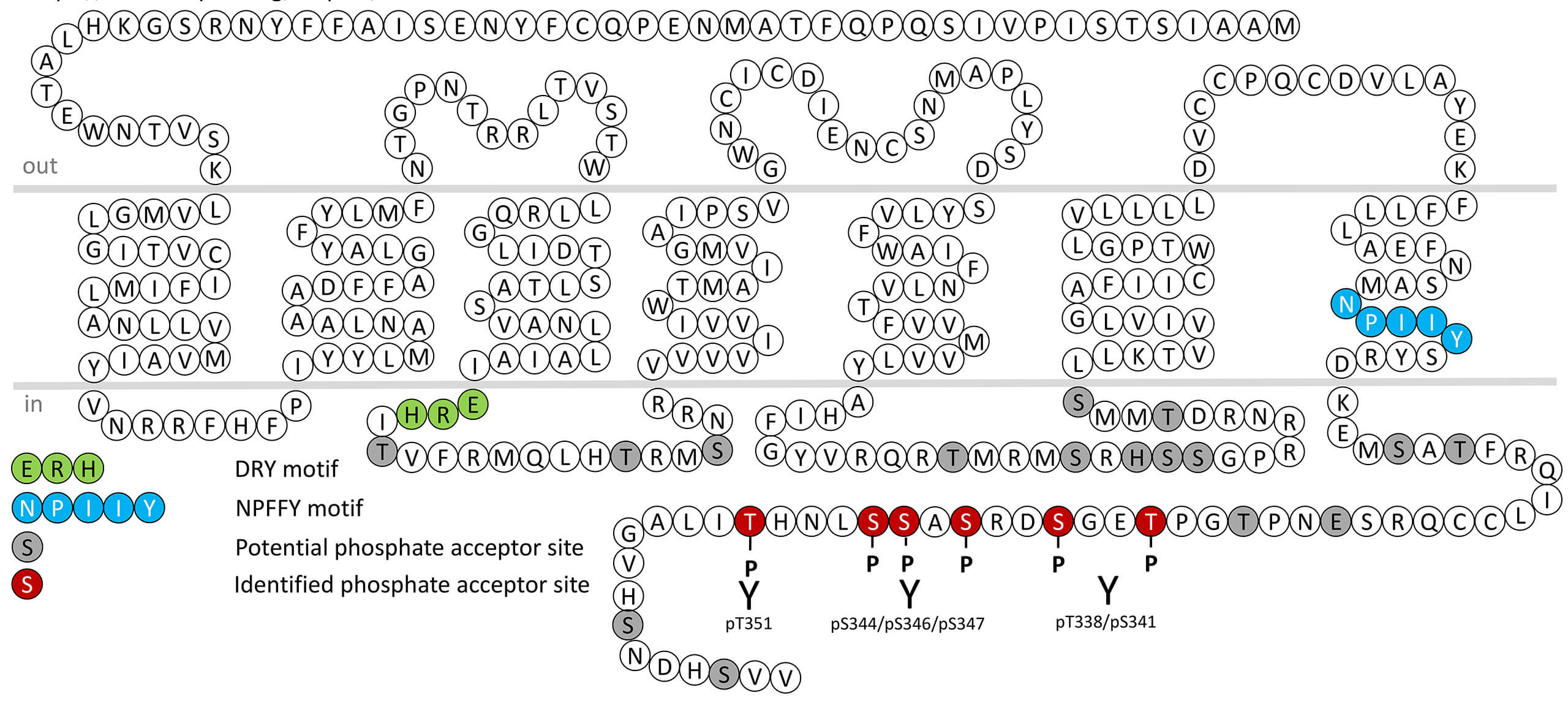 The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA₁), encoded by the LPAR1 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that mediates cellular responses to the bioactive lipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Pharmacologically, LPA₁ couples to multiple G proteins—including Gi/o, Gq/11, and G12/13—activating downstream signaling pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt, which regulate cell proliferation, migration, survival, and cytoskeletal dynamics. LPA₁ is widely expressed across tissues, with high levels in the developing and adult brain, lung, kidney, reproductive organs, and fibroblasts, reflecting its broad physiological roles. Functionally, LPA₁ is crucial for embryonic development, particularly in neuronal differentiation, vascular formation, and myelination, as shown by developmental abnormalities in Lpar1 knockout mice. In adults, LPA₁ contributes to wound healing, fibrosis, pain transmission, and immune cell recruitment, and its dysregulation has been implicated in fibrotic diseases, neuropathic pain, cancer progression, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacological antagonists such as AM095 and BMS-986020 have been developed to inhibit LPA₁ signaling, showing promise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic conditions. The receptor’s ability to respond to lipid mediators links it to metabolic and inflammatory networks. Overall, LPA₁ acts as a key lipid-sensing receptor governing cellular motility, survival, and tissue remodeling, and remains an important therapeutic target in fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. For more information on LPA1 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA₁), encoded by the LPAR1 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that mediates cellular responses to the bioactive lipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Pharmacologically, LPA₁ couples to multiple G proteins—including Gi/o, Gq/11, and G12/13—activating downstream signaling pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt, which regulate cell proliferation, migration, survival, and cytoskeletal dynamics. LPA₁ is widely expressed across tissues, with high levels in the developing and adult brain, lung, kidney, reproductive organs, and fibroblasts, reflecting its broad physiological roles. Functionally, LPA₁ is crucial for embryonic development, particularly in neuronal differentiation, vascular formation, and myelination, as shown by developmental abnormalities in Lpar1 knockout mice. In adults, LPA₁ contributes to wound healing, fibrosis, pain transmission, and immune cell recruitment, and its dysregulation has been implicated in fibrotic diseases, neuropathic pain, cancer progression, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacological antagonists such as AM095 and BMS-986020 have been developed to inhibit LPA₁ signaling, showing promise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic conditions. The receptor’s ability to respond to lipid mediators links it to metabolic and inflammatory networks. Overall, LPA₁ acts as a key lipid-sensing receptor governing cellular motility, survival, and tissue remodeling, and remains an important therapeutic target in fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. For more information on LPA1 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Chun J, Hla T, Lynch KR, Spiegel S, Moolenaar WH. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVIII. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Dec;62(4):579-87. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003111. PMID: 21079037; PMCID: PMC2993255.
Kihara Y, Maceyka M, Spiegel S, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(15):3575-94. doi: 10.1111/bph.12678. Epub 2014 Jul 12. PMID: 24602016; PMCID: PMC4128058.
Blaho V, Chun J, Herr D, Jones D, Jonnalagadda D, Kihara Y. Lysophospholipid (S1P) receptors in GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE. 2023; 2023(1).
 pT338/pS341-LPA1 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...
pT338/pS341-LPA1 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...  pT351-LPA1 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...
pT351-LPA1 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...  pS344/pS346/pS347-LPA1...
pS344/pS346/pS347-LPA1... 
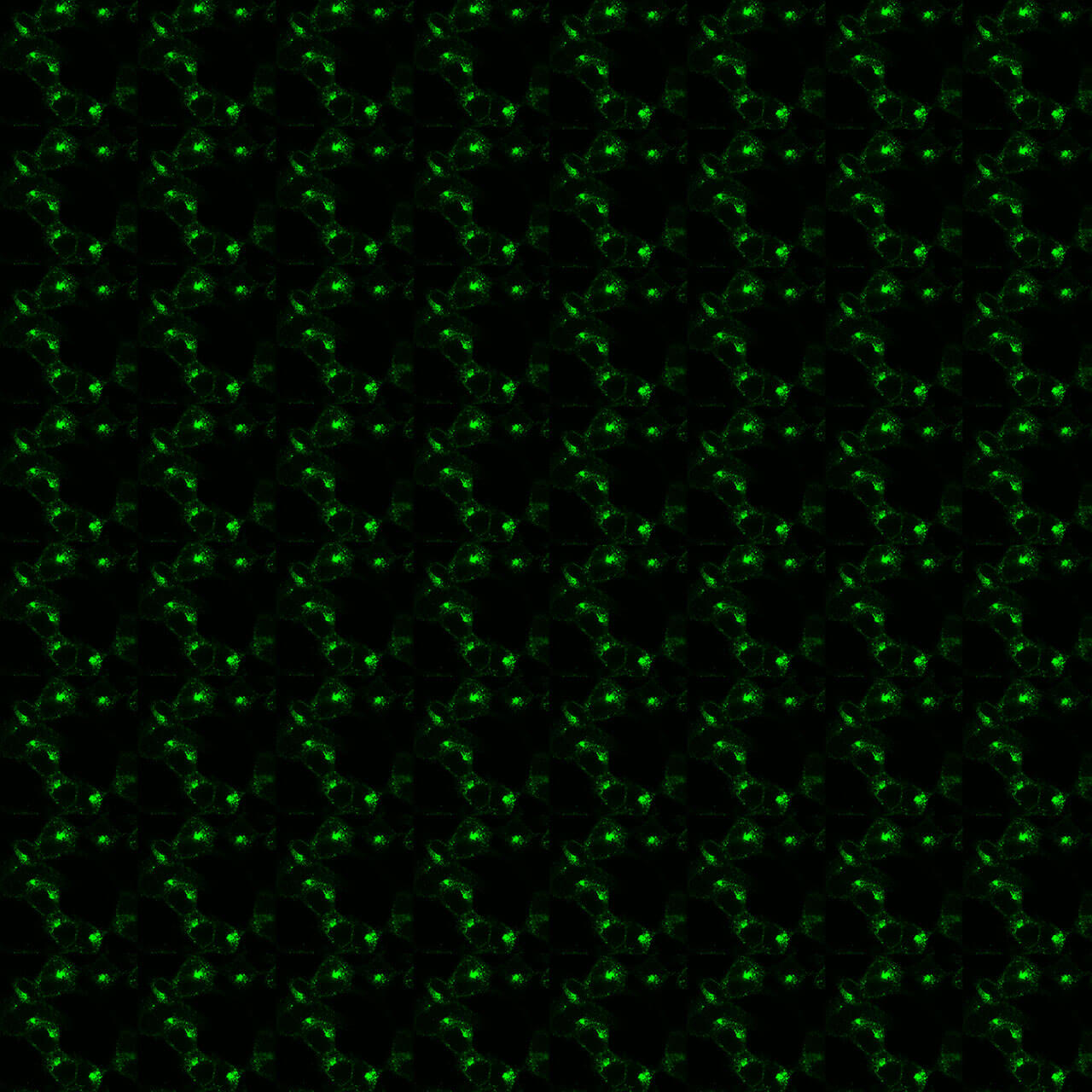
 The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA₁), encoded by the LPAR1 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that mediates cellular responses to the bioactive lipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Pharmacologically, LPA₁ couples to multiple G proteins—including Gi/o, Gq/11, and G12/13—activating downstream signaling pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt, which regulate cell proliferation, migration, survival, and cytoskeletal dynamics. LPA₁ is widely expressed across tissues, with high levels in the developing and adult brain, lung, kidney, reproductive organs, and fibroblasts, reflecting its broad physiological roles. Functionally, LPA₁ is crucial for embryonic development, particularly in neuronal differentiation, vascular formation, and myelination, as shown by developmental abnormalities in Lpar1 knockout mice. In adults, LPA₁ contributes to wound healing, fibrosis, pain transmission, and immune cell recruitment, and its dysregulation has been implicated in fibrotic diseases, neuropathic pain, cancer progression, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacological antagonists such as AM095 and BMS-986020 have been developed to inhibit LPA₁ signaling, showing promise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic conditions. The receptor’s ability to respond to lipid mediators links it to metabolic and inflammatory networks. Overall, LPA₁ acts as a key lipid-sensing receptor governing cellular motility, survival, and tissue remodeling, and remains an important therapeutic target in fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. For more information on LPA1 pharmacology please refer to the
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA₁), encoded by the LPAR1 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that mediates cellular responses to the bioactive lipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Pharmacologically, LPA₁ couples to multiple G proteins—including Gi/o, Gq/11, and G12/13—activating downstream signaling pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/Akt, which regulate cell proliferation, migration, survival, and cytoskeletal dynamics. LPA₁ is widely expressed across tissues, with high levels in the developing and adult brain, lung, kidney, reproductive organs, and fibroblasts, reflecting its broad physiological roles. Functionally, LPA₁ is crucial for embryonic development, particularly in neuronal differentiation, vascular formation, and myelination, as shown by developmental abnormalities in Lpar1 knockout mice. In adults, LPA₁ contributes to wound healing, fibrosis, pain transmission, and immune cell recruitment, and its dysregulation has been implicated in fibrotic diseases, neuropathic pain, cancer progression, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacological antagonists such as AM095 and BMS-986020 have been developed to inhibit LPA₁ signaling, showing promise in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic conditions. The receptor’s ability to respond to lipid mediators links it to metabolic and inflammatory networks. Overall, LPA₁ acts as a key lipid-sensing receptor governing cellular motility, survival, and tissue remodeling, and remains an important therapeutic target in fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer. For more information on LPA1 pharmacology please refer to the