Urotensin Receptor Antibodies
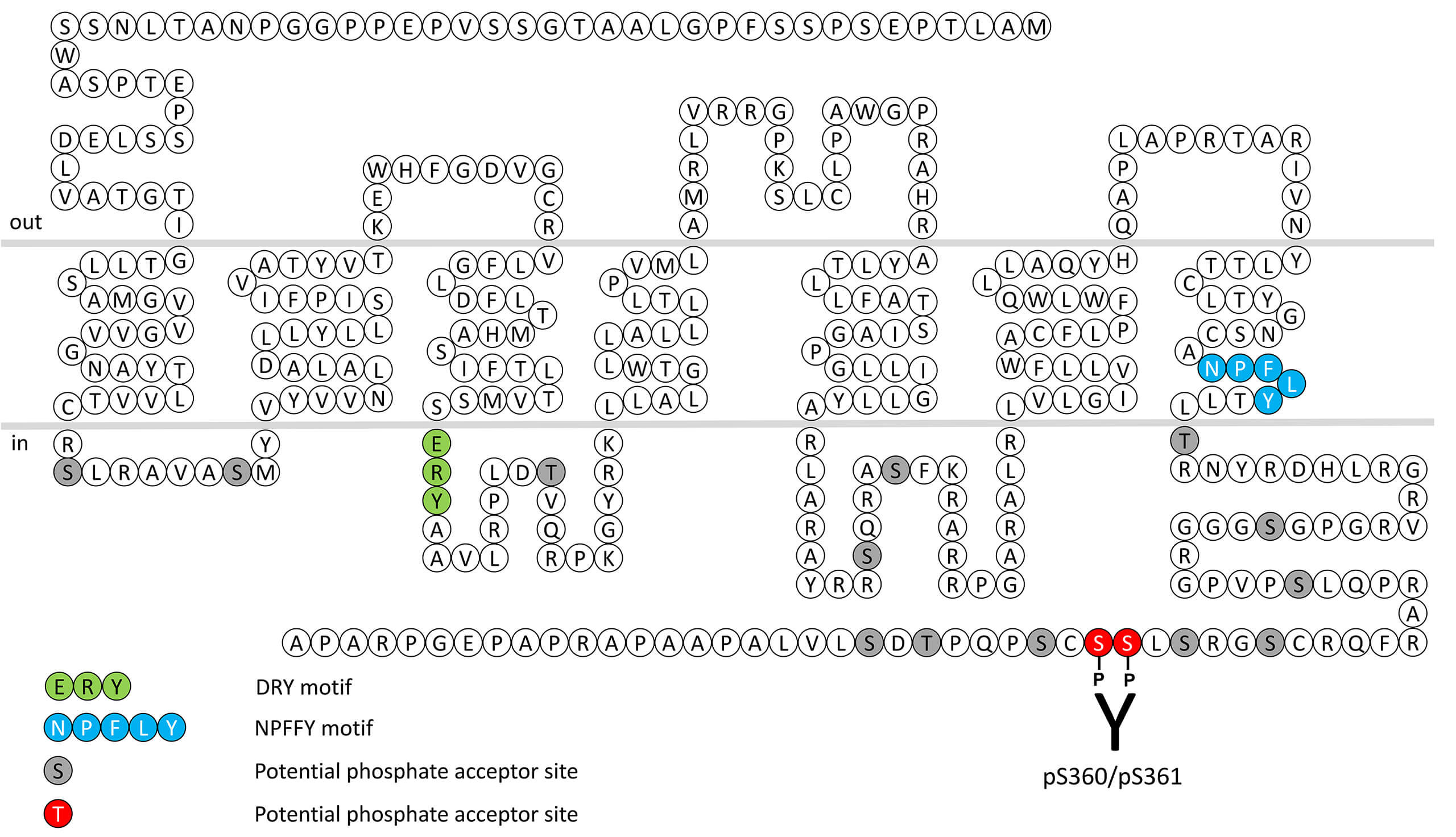
The urotensin-II receptor (UT) is activated by the endogenous dodecapeptide urotensin-II (U-II), originally isolated from the urophysis, the endocrine organ of the caudal neurosecretory system of teleost fish. Human urotensin-II, an 11-amino-acid peptide, retains the cyclohexapeptide sequence that is thought to be important in ligand binding. A second endogenous ligand for the UT has been discovered in rat. This is the urotensin II-related peptide, an octapeptide that is derived from a different gene, but shares the C-terminal sequence (CFWKYCV) common to U-II from other species. The UT receptor exhibits relatively high sequence identity with somatostatin, opioid and galanin receptors.U-II isopeptides are potent and sustained mammalian vasoconstrictors in vitro. This phenomenon is observed primarily in arterial vasculature, consistent with the expression of UT in cardiac and arterial, but not venous, blood vessels and smooth muscle cell lines. Vasoconstriction is resistant to block of adrenergic or cholinergic systems, 5-HT or histamine receptor antagonism. Since responses are reported to be phospholipase-sensitive, such an effect is likely secondary to phosphoinositide metabolism. This is consistent with observations made using recombinant receptors where receptor activation is coupled to Ca2+ and arachidonate hydrolysis in cultured cells. UT receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by phosphorylation of carboxyl-terminal serine360/serine361 (pS360/pS361-UT). This nomenclature refers to the human UT receptor. This phosphorylation motif corresponds to pS363/pS364-UT in mice. For more information on UT receptor pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Vaudry H, Leprince J, Chatenet D, Fournier A, Lambert DG, Le Mével JC, Ohlstein EH, Schwertani A, Tostivint H, Vaudry D. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCII. Urotensin II, urotensin II-related peptide, and their receptor: from structure to function. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(1):214-58. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009480. PMID: 25535277.
 pS360/pS361-UT (phospho-Urotensin Receptor...
pS360/pS361-UT (phospho-Urotensin Receptor...  UT (non-phospho), Urotensin Receptor Antibody
UT (non-phospho), Urotensin Receptor Antibody