Free Fatty Acid Receptor 3 Antibodies
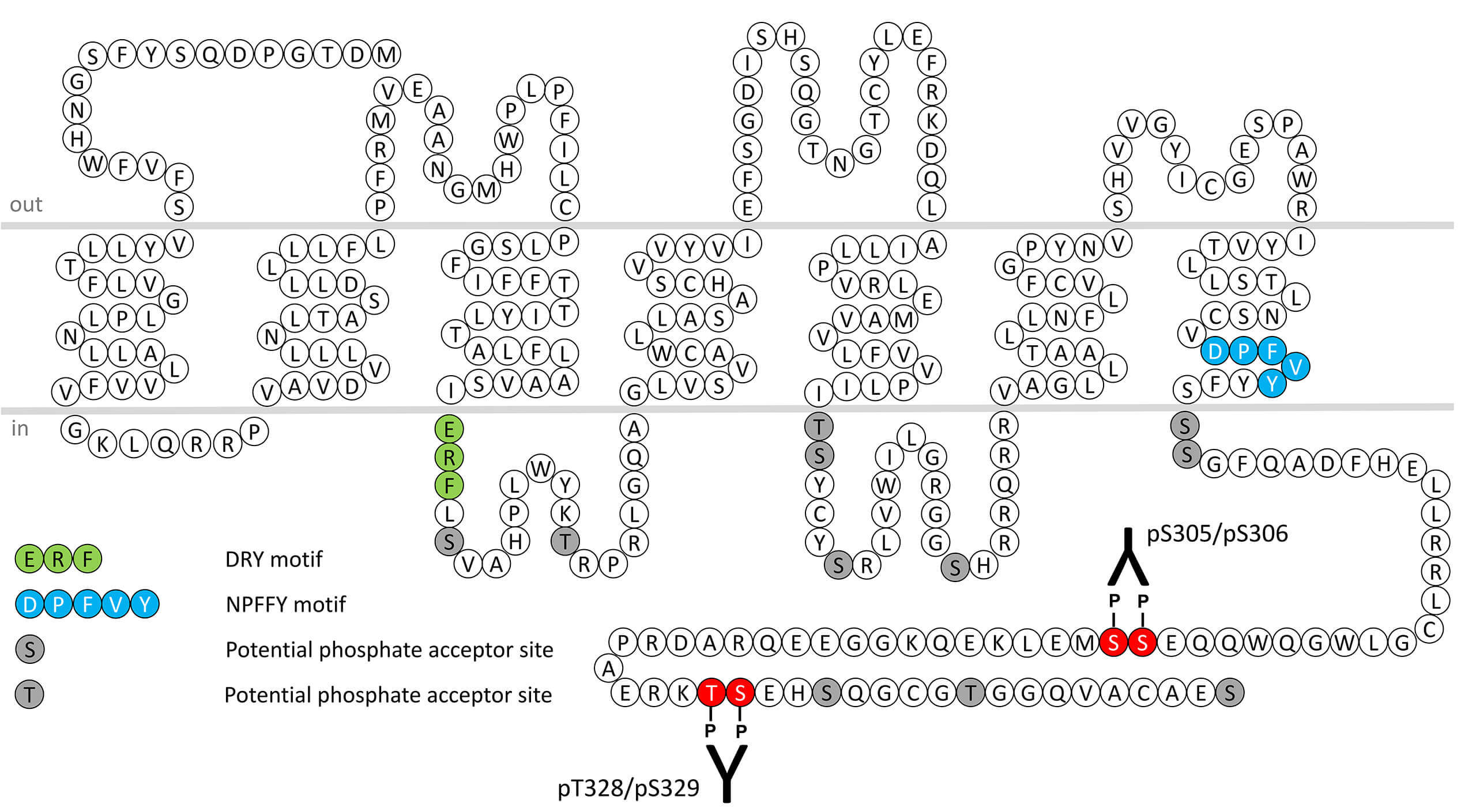
The expression of FFA3 in adipose is supported by expression of the receptor in differentiated human and mouse adipocytes, whilst little expression was observed in pre-adipocytes or brown fat. Moreover, expression of the receptor in various other cell-types including dendritic cells, lymphocytes, peripheral blood mononuclear cells and artery and arteriolar endothelial cells raises further questions as to the role of the receptor in immune cell function. FFA3 differs from FFA2 most notably in its rank order potency of preferred ligands and G protein-coupling. Propionate is the most potent ligand for FFA3 followed by butyrate and pentanoate respectively. Activation of FFA3 by propionate via a pertussis-toxin sensitive Gαi-coupled pathway, was reported to elevate leptin production from mouse adipocytes and primary adipocyte tissue cultures. FFA3 receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by phosphorylation of carboxyl-terminal serine305/serine306 (pS305/pS306-FFA3) and threonine328/serine329 (pT328/pS329-FFA3). This nomenclature refers to the human FFA3 receptor. For more information on FFA3 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Stoddart LA, Smith NJ, Milligan G. International Union of Pharmacology. LXXI. Free fatty acid receptors FFA1, -2, and -3: pharmacology and pathophysiological functions. Pharmacol Rev. 2008 Dec;60(4):405-17. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.00802. Epub 2008 Dec 1. PMID: 19047536.
Riddy DM, Delerive P, Summers RJ, Sexton PM, Langmead CJ. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Targeting Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmacol Rev. 2018 Jan;70(1):39-67. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.014373. PMID: 29233848.
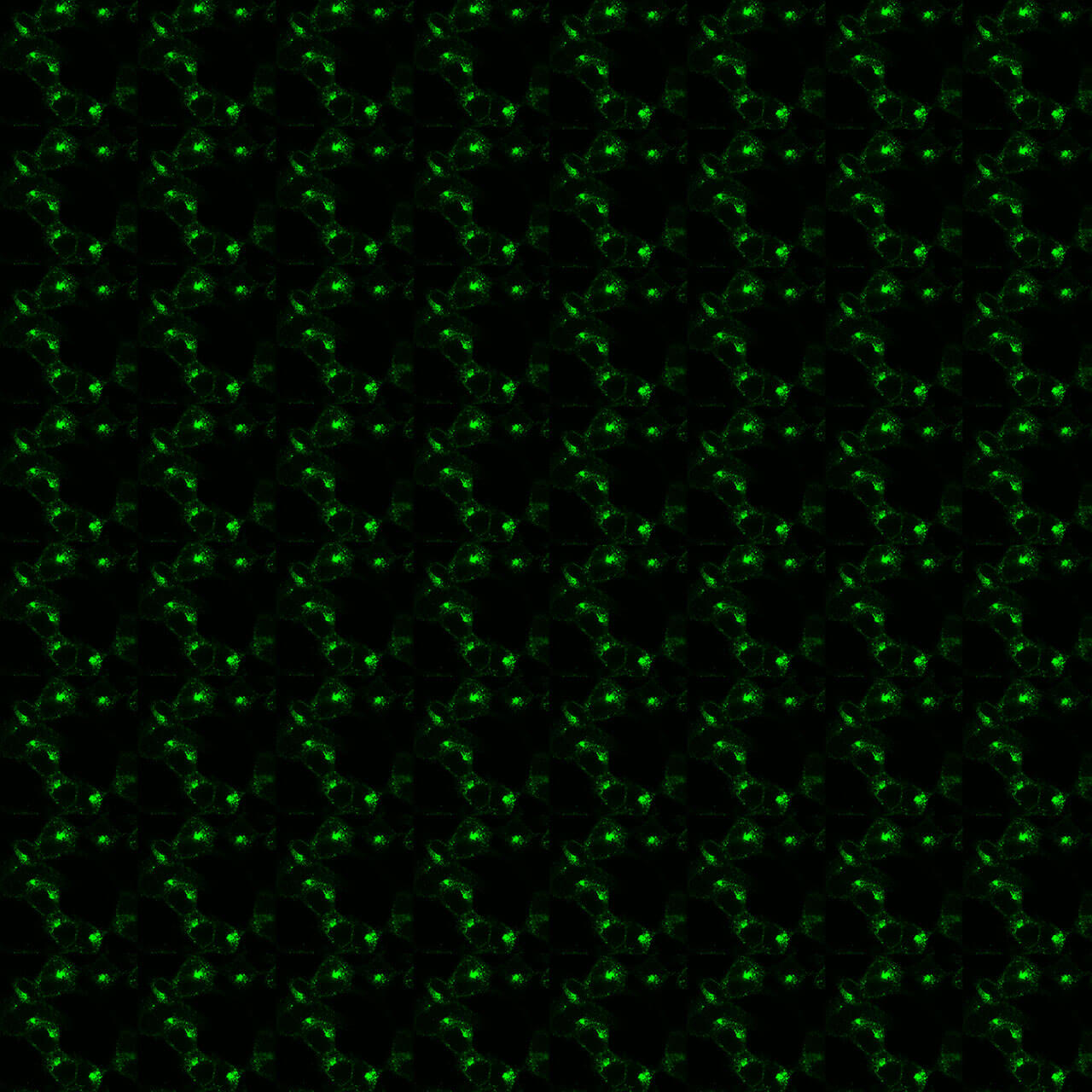
 pS305/pS306-FFA3 (phospho-FFA3 Antibody)
pS305/pS306-FFA3 (phospho-FFA3 Antibody)  pT328/pS329-FFA3 (phospho-FFA3 Antibody)
pT328/pS329-FFA3 (phospho-FFA3 Antibody)