Bombesin Receptor 3 Antibodies
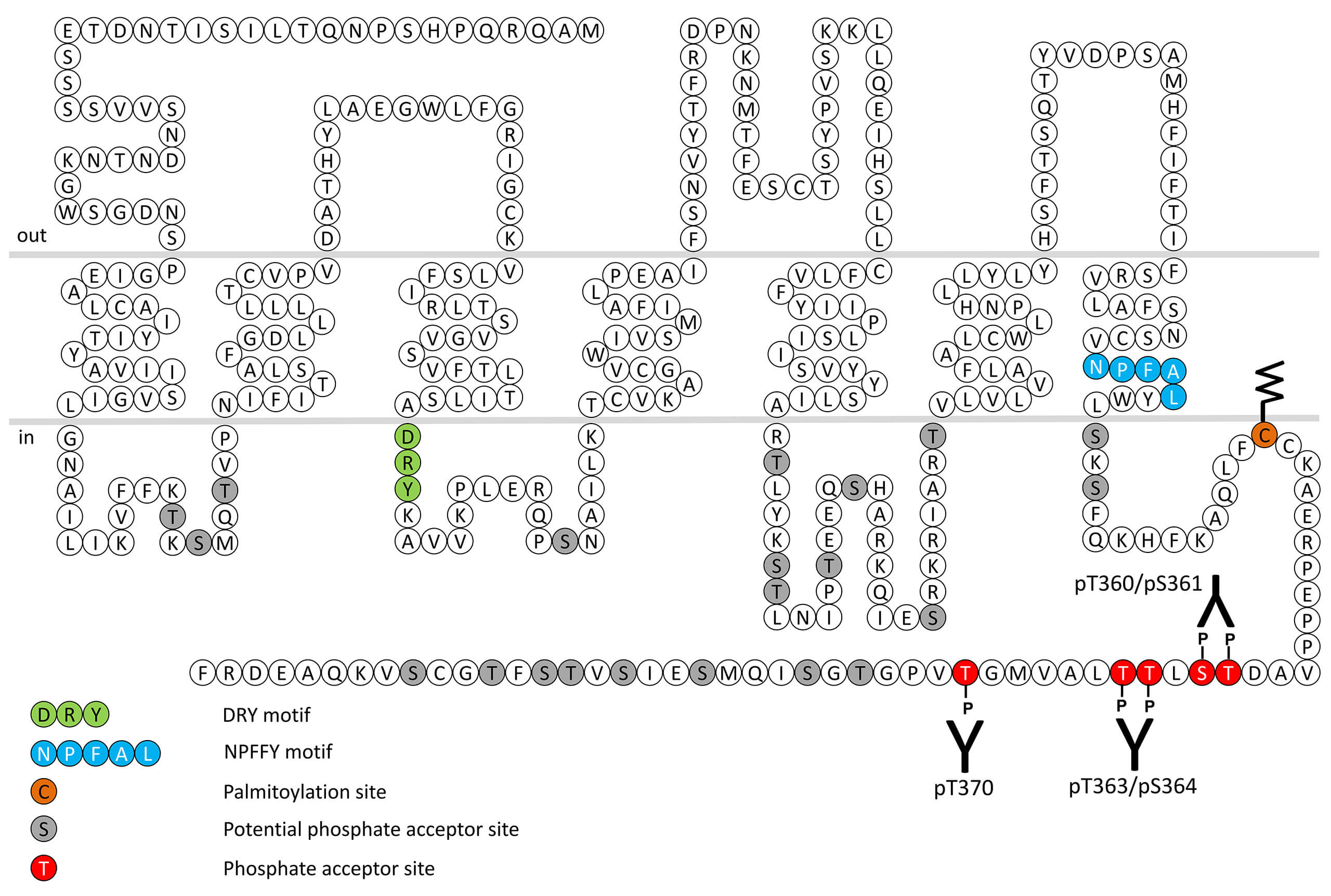
The natural ligand for the BB3 receptor remains unknown. Nevertheless it has been found that the synthetic bombesin analogs can bind and activate BB3 receptors. Recently a number of BB3 receptor nonpeptide agonists have been described including derivatives of omeprazole. Because the natural ligand of the BB3 receptor is not known most of the information on the possible physiological or pathophysiological role of this receptor has come from BB3 receptor knockout studies. BB3 receptor knockout mice develop mild obesity, associated with hypertension and impairment of glucose metabolism. These changes were associated with increased feeding behaviour, reduced metabolic rate, increased serum leptin and hyperphagia. These results suggested the BB3 receptor could play a role in energy balance, weight control and control of blood glucose levels. BB3 receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by phosphorylation of carboxyl-terminal threonine360/serine361 (pT360/pS361-BB3), threonine363/threonine364 (pT363/pT364-BB3) and threonine370 (pT370-BB3). This nomenclature refers to the human BB3 receptor. For more information on BB3 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Jensen RT, Battey JF, Spindel ER, Benya RV. International Union of Pharmacology. LXVIII. Mammalian bombesin receptors: nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, signaling, and functions in normal and disease states. Pharmacol Rev. 2008 Mar;60(1):1-42. doi: 10.1124/pr.107.07108. Epub 2007 Nov 30. PMID: 18055507; PMCID: PMC2517428.
 pT363/pT364-BB3 Phosphorylation Assay Kit
pT363/pT364-BB3 Phosphorylation Assay Kit  pT360/pS361-BB3 Phosphorylation Assay Kit
pT360/pS361-BB3 Phosphorylation Assay Kit