No results were found for the filter!
NEW
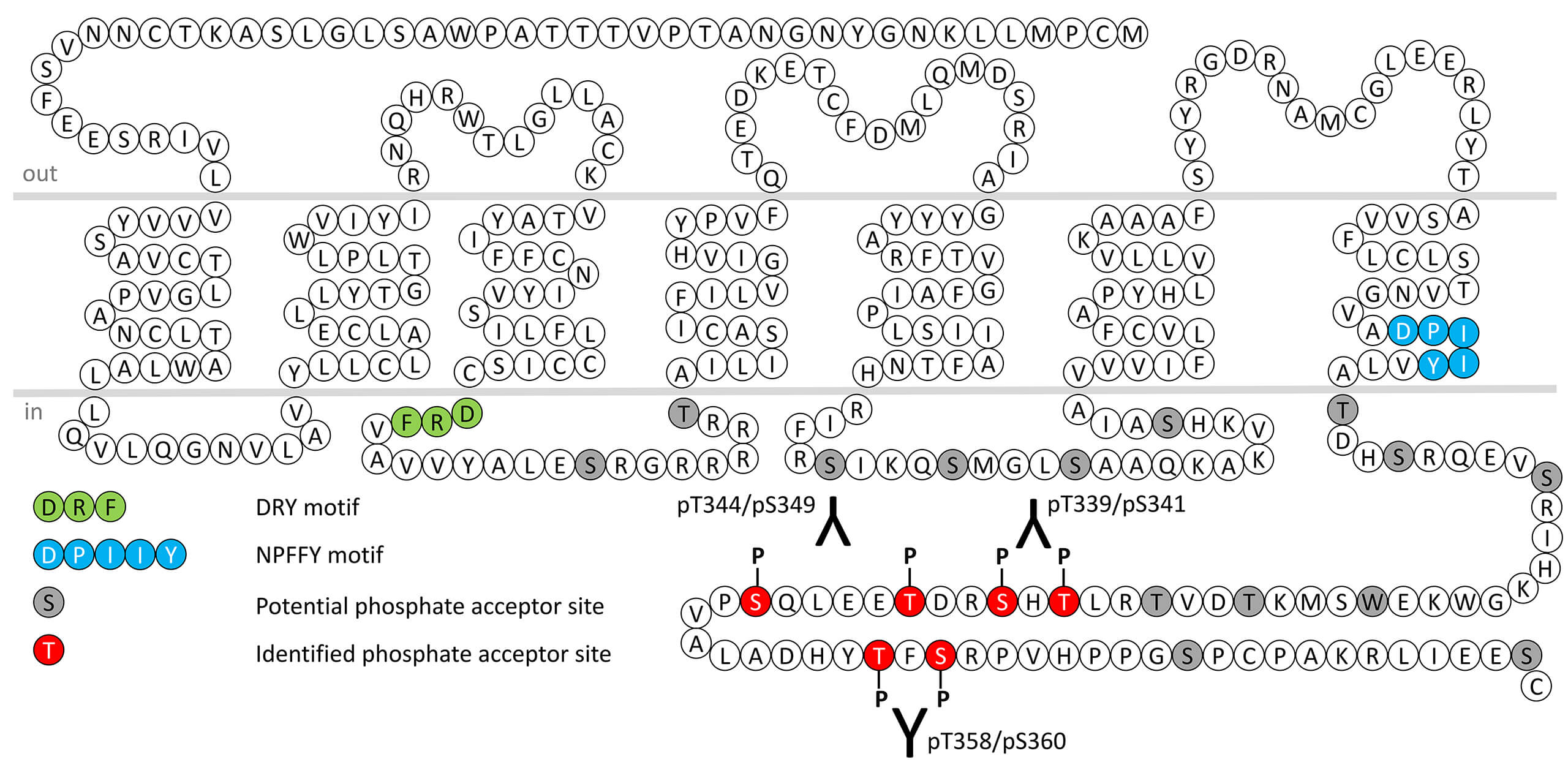
 pT339/pS341-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody)
pT339/pS341-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody) Threonine339/Serine341 (T339/S341) is major phosphorylation site of human GPR132 receptor. The pT339/pS341-GPR132 antibody detects phosphorylation in response to agonists. T339/S341 phosphorylation is likely to be involved in efficient...
$ 375.00 *
NEW
 pT344/pS349-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody)
pT344/pS349-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody) Threonine344/Serine349 (T344/S349) is major phosphorylation site of human GPR132 receptor. The pT344/pS349-GPR132 antibody detects phosphorylation in response to agonists. T344/S349 phosphorylation is likely to be involved in efficient...
$ 375.00 *
NEW
 pT358/pS360-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody)
pT358/pS360-GPR132 (phospho-GPR132 Antibody) Threonine358/Serine360 (T358/S360) is major phosphorylation site of human GPR132 receptor. The pT358/pS360-GPR132 antibody detects phosphorylation in response to agonists. T358/S360 phosphorylation is likely to be involved in efficient...
$ 375.00 *
Recently viewed