Calcitonin Receptor Antibodies
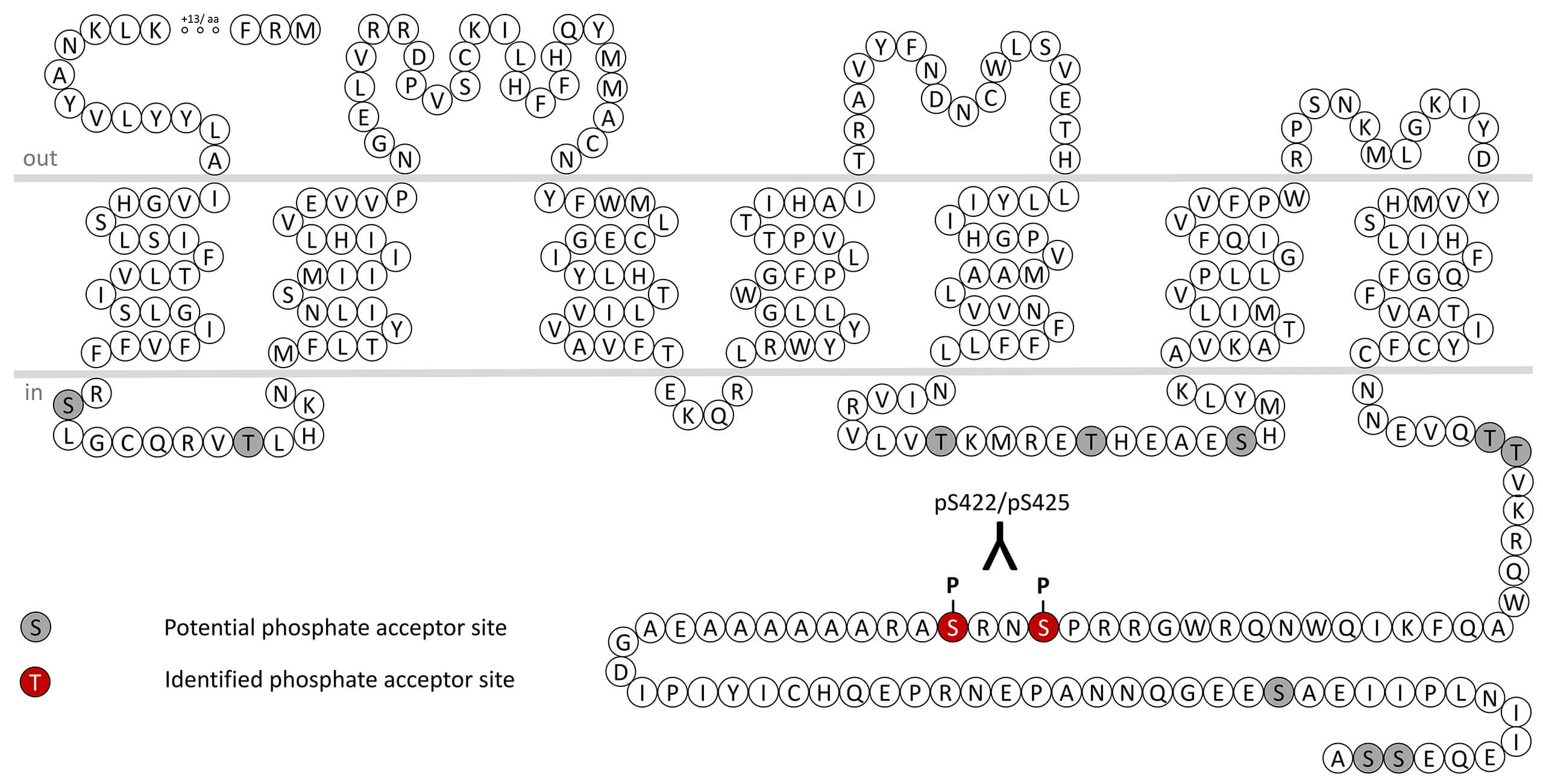
The calcitonin receptor (CT) is a conventional class B GPCR. This receptor also interacts with RAMPs to form several subtypes of high affinity amylin receptor which have significant affinity for CGRP. The most well-known action of calcitonin is the regulation of bone metabolism, in particular the inhibition of bone resorption by osteoclasts. Global CT receptor deletion results in embryonic death prior to initiation of skeletogenesis. Together with data on knockout of calcitonin/CGRP gene, the data are supportive of a role for calcitonin and its receptor in the formation and resorption aspects of bone metabolism under physiological conditions. CT receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by phosphorylation of carboxyl-terminal serine422/serine425 (pS422/pS425-CT). This nomenclature refers to the human CT receptor. For more information on CT receptor pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Hay DL, Garelja ML, Poyner DR, Walker CS. Update on the pharmacology of calcitonin/CGRP family of peptides: IUPHAR Review 25. Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;175(1):3-17. doi: 10.1111/bph.14075. Epub 2017 Nov 28. PMID: 29059473; PMCID: PMC5740251.
Hay DL, Chen S, Lutz TA, Parkes DG, Roth JD. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol Rev. 2015 Jul;67(3):564-600. doi: 10.1124/pr.115.010629. PMID: 26071095.
Garelja ML, Hay D, Poyner DR, Walker CS. Calcitonin receptors in GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE. 2023; 2023(1). Available from: https://doi.org/10.2218/gtopdb/F11/2023.1.
 pS422/pS425-CT (phospho-Calcitonin Receptor...
pS422/pS425-CT (phospho-Calcitonin Receptor...