Immuno-Grade Parathyroid Hormone Receptor 1 Antibodies
The parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTH1) is the specific receptor for the 84-amino acid peptide PTH. PTH acts primarily on kidney and bone. In the kidney, PTH stimulates the reabsorption of calcium in the distal convoluted tubule. It also leads to an enhancement of 1a-hydroxylase activity. In bone, PTH induces calcium release by acting indirectly on osteoclasts. The direct stimulatory effect on osteoblasts leads to an increase in bone mass. In addition to calcium homoeostasis, PTH also regulates blood phosphate concentration by inhibition of tubular phosphate reabsorption in the kidney. PTH1 receptors are expressed at the basolateral plasma membrane of epithelial cells in the proximal and distal tubules of the kidney. In bone, PTH1 receptors are seen as discrete plasma membrane staining of osteocytes and osteoblasts. PTH1 is also expressed in the gut and in a number of neoplastic tissues including colorectal carcinoma, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma and osteosarcoma.
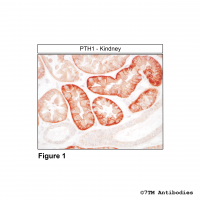 PTH1 (IHC-grade), Parathyroid Hormone Receptor...
PTH1 (IHC-grade), Parathyroid Hormone Receptor...