Immuno-Grade µ-Opioid Receptor Antibodies
The µ-opioid receptor (MOP) is the primary target for many potent analgesics used in the clinic including morphine, oxycodone, hydromorphone, fentanyl sufentanil and methadone. MOP is expressed on neuronal cell bodies and fibers in distinct regions of the central and peripheral nervous system. In the CNS, MOP is abundant in the cortex, amygdala, hippocampus, caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, thalamus, medial habenula, fasciculus retroflexus, interpeduncular nucleus, substantia nigra, superior and inferior colliculus, parabrachial nucleus, locus coeruleus, nucleus of the solitary tract, the superficial layers of the spinal cord dorsal horn as well as in the dorsal root ganglia (predominantly small- and medium-size cells). In the periphery, MOP is present in intramural ganglia of the gut and ganglion cells within the adrenal medulla.
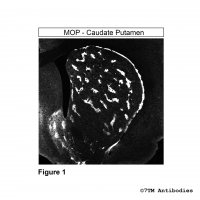 MOP (IHC-grade), µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody
MOP (IHC-grade), µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody