Neurotensin Receptor 1 Antibodies
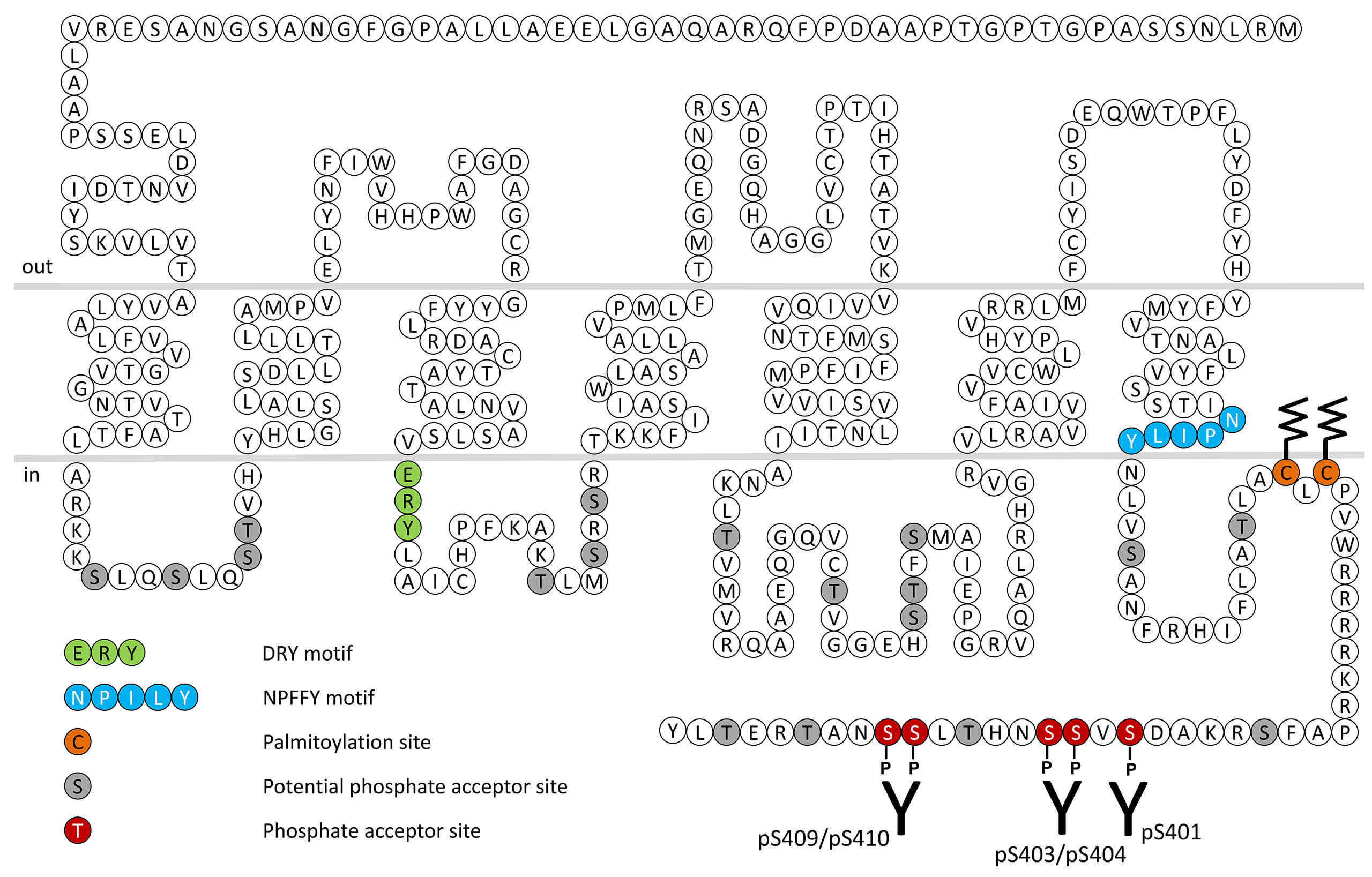
NTS1 is expressed mainly in the brain and intestine. In the rat brain, high levels of NTS1 are found in neurons of the diagonal band of Broca, medial septal nucleus, magnocellular preoptic area, suprachiasmatic nucleus, substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area. NTS1 is selectively expressed by central dopamine neurons and is clearly associated with mesolimbic and mesocortical systems. With regard to G protein-coupling, NTS1 is a Gq-preferring receptor in almost all systems examined. Activation of NTS1 is probably responsible for the observed effects of NT on cancer cell proliferation and food intake. However, the most convincing implication of NTS1 is related to the NT-dopamine interactions in the brain. Indeed, NT modulates dopamine transmisssion in the nigro-striatal and mesocorticolimbic pathways through NTS1, indicating that NT analogues specifically targeting this receptor might represent a new class of antipsychotic drugs. NTS1 receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by a proximal phosphorylation cluster namely carboxyl-terminal serine401 (pS401-NTS1) and serine403/serine404 (pS403/pS404-NTS1) and a distal phosphorylation cluster namely serine409/serine410 (pS409/pS410-NTS1). This nomenclature refers to the human NTS1 receptor. For more information on NTS1 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Mazella J, Sarret P, Vincent JP. Neurotensin receptors (version 2019.4) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE. 2019; 2019(4). Available from: https://doi.org/10.2218/gtopdb/F47/2019.4
 pS409/pS410-NTS1 (IHC-grade phospho-Neurotensin...
pS409/pS410-NTS1 (IHC-grade phospho-Neurotensin...