Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2 Antibodies
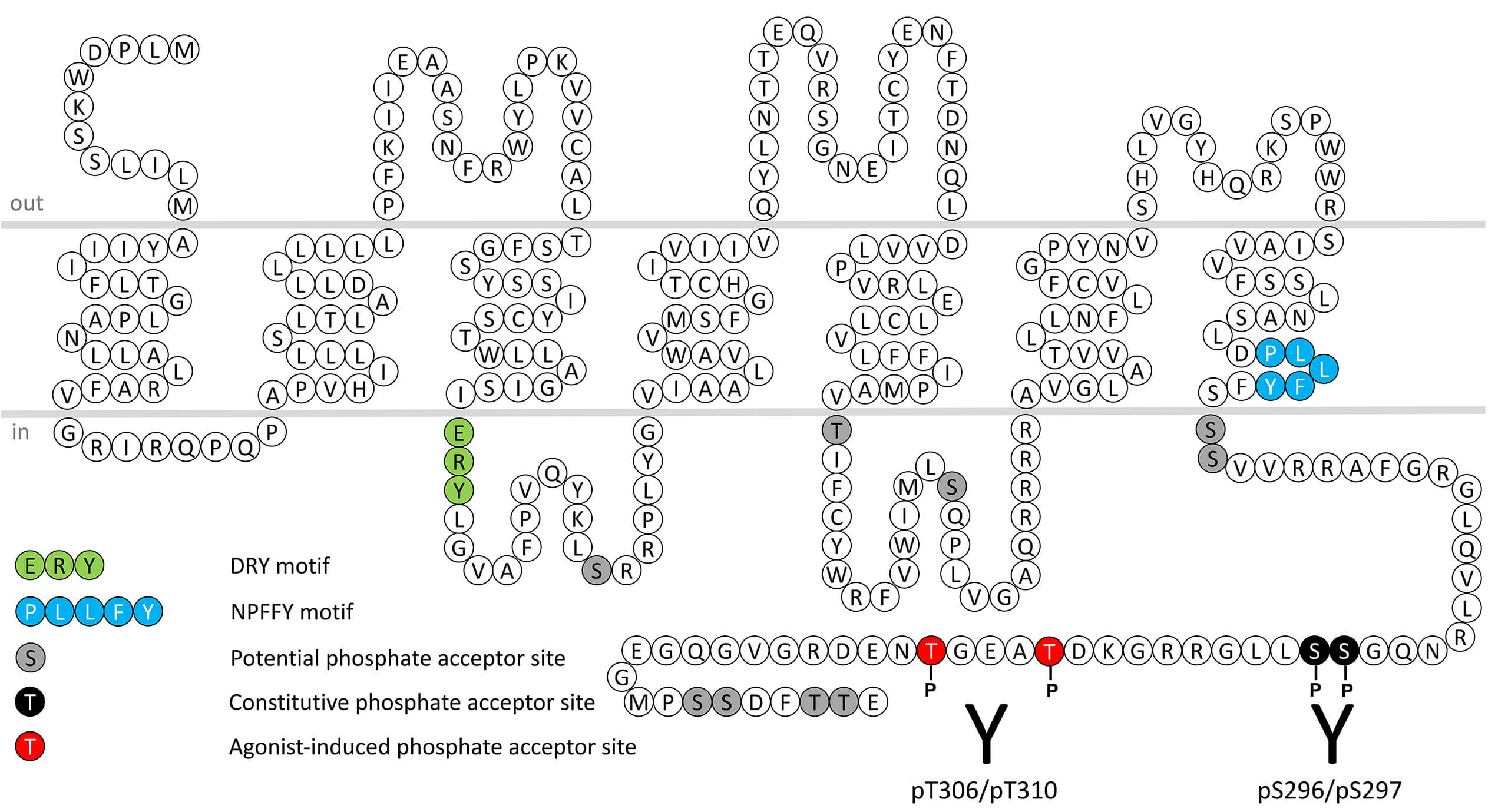
FFA2 is predominantly expressed in adipose, inflammatory cells and the GI-tract. Elevation of FFA2 expression was observed in adipose of mice fed a high-fat diet compared that of mice on a low-fat diet suggesting a role in adipogenesis. FFA2 may be involved in the regulation of GI gastrointestinal motility and secretion since the receptor co-localizes with PYY in mucosal epithelium and mast cells. Expression of FFA2 has also been described in mouse pancreas with increased expression in islets from db/db and ob/ob mice. FFA2 is mainly coupled to Gαq. Acetate and propionate are the most potent ligands for the receptor with pentanoate less active. FFA2 receptor desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization are regulated by phosphorylation of carboxyl-terminal serine296/serine297 (pS296/pS297-FFA2) and threonine306/threonine310 (pT306/pT310-FFA2). This nomenclature refers to the human FFA2 receptor. For more information on FFA2 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Stoddart LA, Smith NJ, Milligan G. International Union of Pharmacology. LXXI. Free fatty acid receptors FFA1, -2, and -3: pharmacology and pathophysiological functions. Pharmacol Rev. 2008 Dec;60(4):405-17. doi: 10.1124/pr.108.00802. Epub 2008 Dec 1. PMID: 19047536.
Riddy DM, Delerive P, Summers RJ, Sexton PM, Langmead CJ. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Targeting Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmacol Rev. 2018 Jan;70(1):39-67. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.014373. PMID: 29233848.
 pS296/pS297-FFA2 (IHC-grade phospho-FFA2 Antibody)
pS296/pS297-FFA2 (IHC-grade phospho-FFA2 Antibody)  pT306/pT310-FFA2 (IHC grade phospho-FFA2 Antibody)
pT306/pT310-FFA2 (IHC grade phospho-FFA2 Antibody)