No results were found for the filter!
Citations
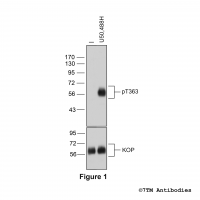 pT363-KOP (phospho-κ-Opioid Receptor Antibody)
pT363-KOP (phospho-κ-Opioid Receptor Antibody) Threonine363 is a major phosphorylation site of the kappa-opioid receptor (KOP). The pT363-KOP antibody detects phosphorylation in response to high-efficacy agonists. T363 phosphorylation is a key regulator of KOP desensitization,...
$ 375.00 *
Citations
KO-Validated
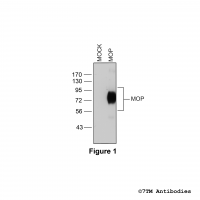 MOP (non-phospho), µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody
MOP (non-phospho), µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody The non-phospho-µ-opioid receptor antibody is directed against the distal end of the carboxyl-terminal tail of mouse, rat and human MOP. It detects selectively the canonical form of MOP and none of the putative splice variants. It can be...
$ 375.00 *
Citations
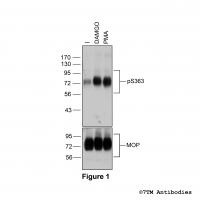 pS363-MOP (phospho-µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody)
pS363-MOP (phospho-µ-Opioid Receptor Antibody) Serine363 (S363) is a constitutive phosphorylation site of the µ-opioid receptor (MOP). The pT363-MOP antibody detects phosphorylated MOP in cultured cells. S363 is a substrate for PKC-mediated phosphorylation.
$ 375.00 *
Recently viewed