LPA4 Receptor Antibodies
 The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 (LPA₄), encoded by the LPAR4 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), although with distinct signaling properties compared to the classical LPA₁–₃ receptors. LPA₄ couples to multiple G proteins, including G12/13, Gq/11, and Gs, activating pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and cAMP production, which regulate cell shape, motility, proliferation, and differentiation. LPA₄ is expressed in a range of tissues, including bone, lung, spleen, heart, and the nervous system, as well as in endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells, highlighting roles in development and tissue homeostasis. Functionally, LPA₄ has been implicated in vascular development, osteogenesis, and neural differentiation, and it can modulate cell adhesion and migration differently from LPA₁–₃, often exerting inhibitory effects on motility in certain cell types. In pathological contexts, LPA₄ may influence cancer progression, fibrosis, and vascular remodeling, although its role is less well characterized than LPA₁–₃. Pharmacological studies using synthetic agonists and receptor knockouts have helped define its contribution to stem cell differentiation and tissue morphogenesis. LPA₄ also demonstrates cross-talk with other LPA receptors, adding complexity to lipid signaling networks. Overall, LPA₄ acts as a versatile lipid-sensing receptor involved in development, tissue architecture, and cell motility regulation, with potential implications for regenerative medicine and disease modulation. For more information on LPA4 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 (LPA₄), encoded by the LPAR4 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), although with distinct signaling properties compared to the classical LPA₁–₃ receptors. LPA₄ couples to multiple G proteins, including G12/13, Gq/11, and Gs, activating pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and cAMP production, which regulate cell shape, motility, proliferation, and differentiation. LPA₄ is expressed in a range of tissues, including bone, lung, spleen, heart, and the nervous system, as well as in endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells, highlighting roles in development and tissue homeostasis. Functionally, LPA₄ has been implicated in vascular development, osteogenesis, and neural differentiation, and it can modulate cell adhesion and migration differently from LPA₁–₃, often exerting inhibitory effects on motility in certain cell types. In pathological contexts, LPA₄ may influence cancer progression, fibrosis, and vascular remodeling, although its role is less well characterized than LPA₁–₃. Pharmacological studies using synthetic agonists and receptor knockouts have helped define its contribution to stem cell differentiation and tissue morphogenesis. LPA₄ also demonstrates cross-talk with other LPA receptors, adding complexity to lipid signaling networks. Overall, LPA₄ acts as a versatile lipid-sensing receptor involved in development, tissue architecture, and cell motility regulation, with potential implications for regenerative medicine and disease modulation. For more information on LPA4 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database. For further reading refer to:
Chun J, Hla T, Lynch KR, Spiegel S, Moolenaar WH. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVIII. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Dec;62(4):579-87. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003111. PMID: 21079037; PMCID: PMC2993255.
Kihara Y, Maceyka M, Spiegel S, Chun J. Lysophospholipid receptor nomenclature review: IUPHAR Review 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(15):3575-94. doi: 10.1111/bph.12678. Epub 2014 Jul 12. PMID: 24602016; PMCID: PMC4128058.
Blaho V, Chun J, Herr D, Jones D, Jonnalagadda D, Kihara Y. Lysophospholipid (S1P) receptors in GtoPdb v.2023.1. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE. 2023; 2023(1).
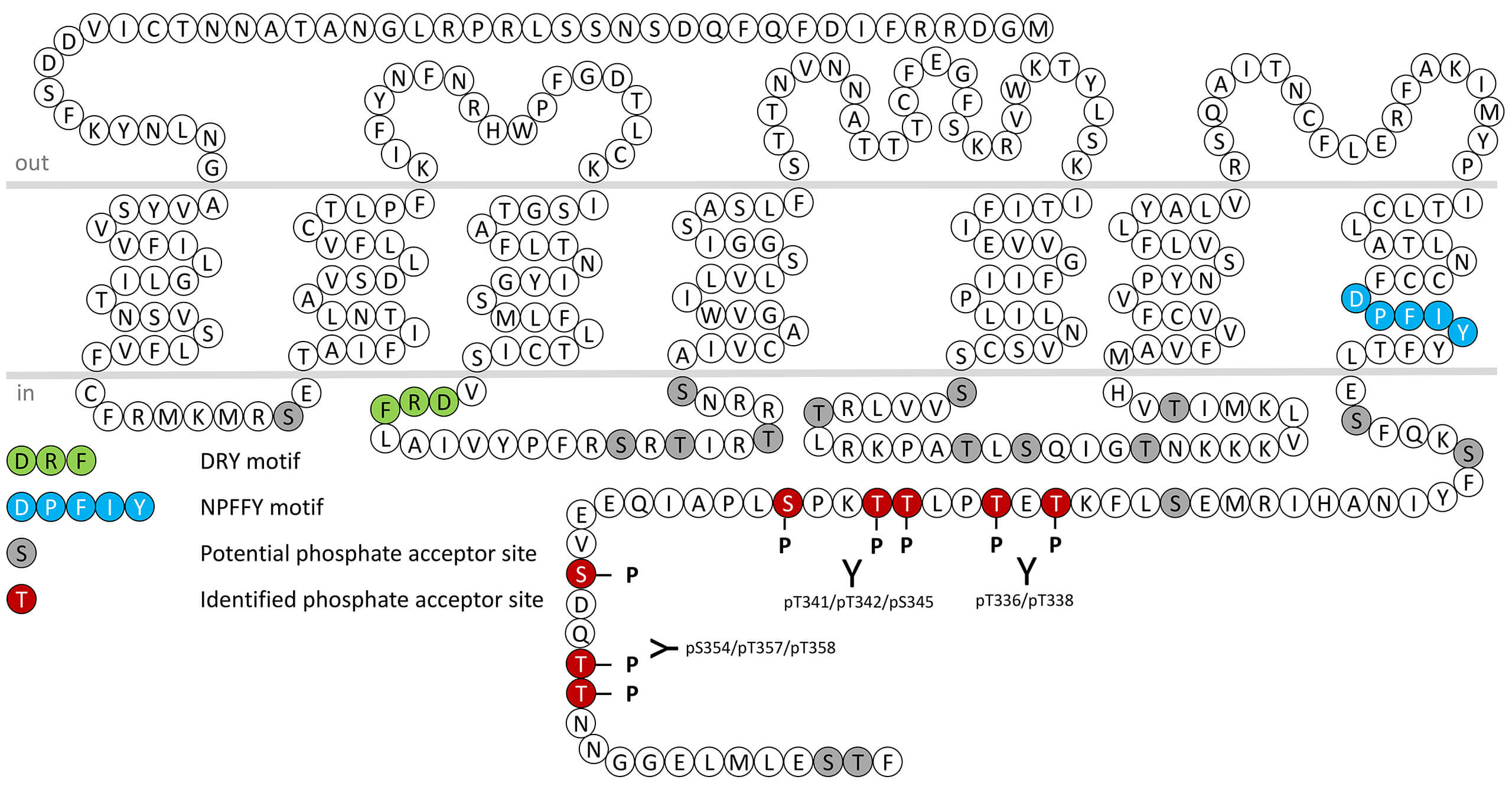
 pT336/pT338-LPA4 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...
pT336/pT338-LPA4 (phospho-Lysophosphatidic Acid...  pS354/pT357/pT358-LPA4...
pS354/pT357/pT358-LPA4...  pT341/pT342/pS345-LPA4...
pT341/pT342/pS345-LPA4... 
 The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 (LPA₄), encoded by the LPAR4 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), although with distinct signaling properties compared to the classical LPA₁–₃ receptors. LPA₄ couples to multiple G proteins, including G12/13, Gq/11, and Gs, activating pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and cAMP production, which regulate cell shape, motility, proliferation, and differentiation. LPA₄ is expressed in a range of tissues, including bone, lung, spleen, heart, and the nervous system, as well as in endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells, highlighting roles in development and tissue homeostasis. Functionally, LPA₄ has been implicated in vascular development, osteogenesis, and neural differentiation, and it can modulate cell adhesion and migration differently from LPA₁–₃, often exerting inhibitory effects on motility in certain cell types. In pathological contexts, LPA₄ may influence cancer progression, fibrosis, and vascular remodeling, although its role is less well characterized than LPA₁–₃. Pharmacological studies using synthetic agonists and receptor knockouts have helped define its contribution to stem cell differentiation and tissue morphogenesis. LPA₄ also demonstrates cross-talk with other LPA receptors, adding complexity to lipid signaling networks. Overall, LPA₄ acts as a versatile lipid-sensing receptor involved in development, tissue architecture, and cell motility regulation, with potential implications for regenerative medicine and disease modulation. For more information on LPA4 pharmacology please refer to the
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor 4 (LPA₄), encoded by the LPAR4 gene, is a class A G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), although with distinct signaling properties compared to the classical LPA₁–₃ receptors. LPA₄ couples to multiple G proteins, including G12/13, Gq/11, and Gs, activating pathways such as RhoA, phospholipase C (PLC), MAPK/ERK, and cAMP production, which regulate cell shape, motility, proliferation, and differentiation. LPA₄ is expressed in a range of tissues, including bone, lung, spleen, heart, and the nervous system, as well as in endothelial and mesenchymal stem cells, highlighting roles in development and tissue homeostasis. Functionally, LPA₄ has been implicated in vascular development, osteogenesis, and neural differentiation, and it can modulate cell adhesion and migration differently from LPA₁–₃, often exerting inhibitory effects on motility in certain cell types. In pathological contexts, LPA₄ may influence cancer progression, fibrosis, and vascular remodeling, although its role is less well characterized than LPA₁–₃. Pharmacological studies using synthetic agonists and receptor knockouts have helped define its contribution to stem cell differentiation and tissue morphogenesis. LPA₄ also demonstrates cross-talk with other LPA receptors, adding complexity to lipid signaling networks. Overall, LPA₄ acts as a versatile lipid-sensing receptor involved in development, tissue architecture, and cell motility regulation, with potential implications for regenerative medicine and disease modulation. For more information on LPA4 pharmacology please refer to the