RXFP4 Receptor Antibodies
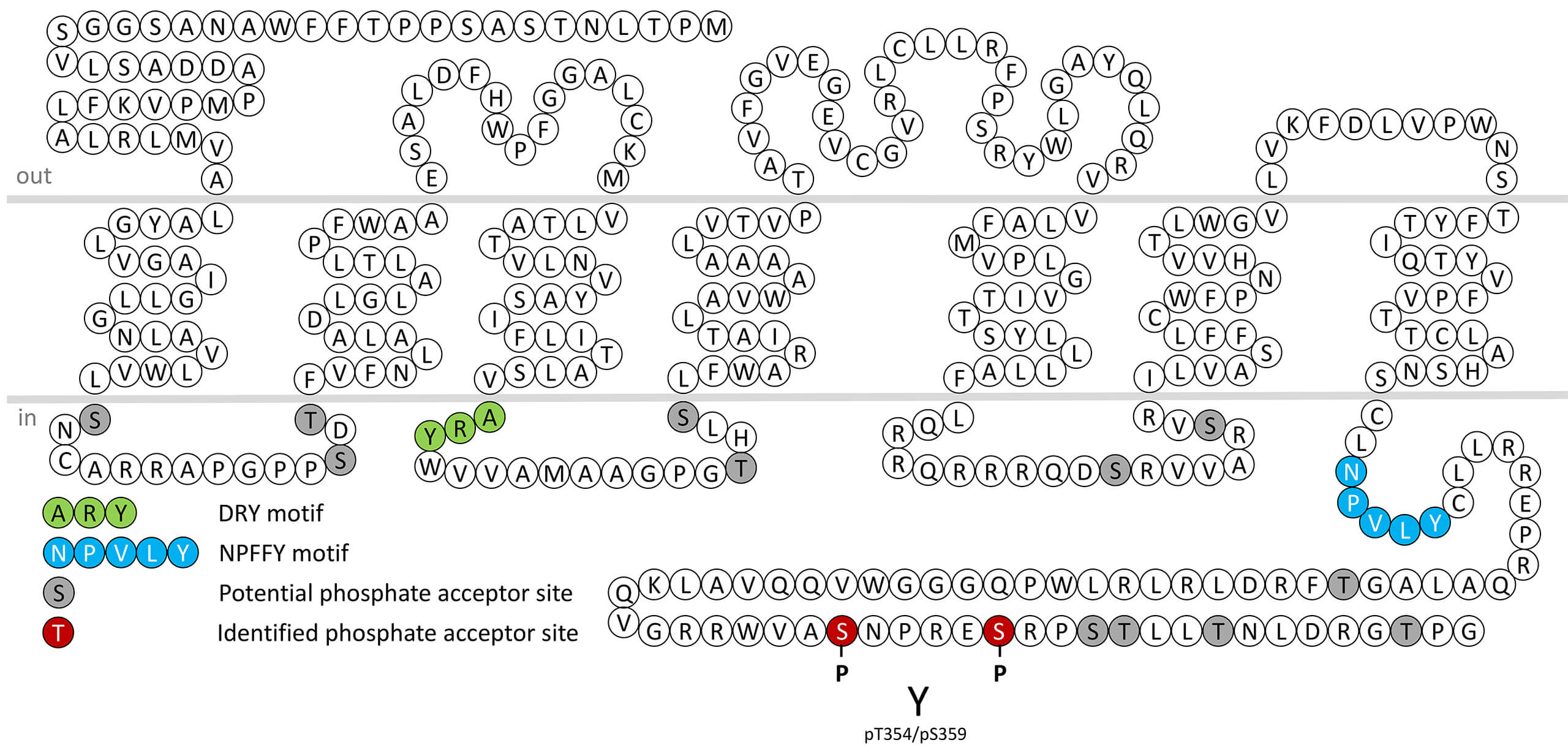 RXFP4 (relaxin family peptide receptor 4) is a G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that primarily binds insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5), a member of the relaxin/insulin peptide family. Pharmacologically, RXFP4 couples predominantly to Gi/o proteins, resulting in inhibition of adenylate cyclase and reduced cyclic AMP (cAMP) production, although additional signaling pathways such as ERK1/2 activation have also been described. RXFP4 expression is mainly localized to the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the colon and rectum, but is also detected in the hypothalamus, pancreas, and adipose tissue, suggesting both peripheral and central roles. Functionally, the INSL5–RXFP4 system is implicated in the regulation of appetite, energy homeostasis, and gut motility. Activation of RXFP4 has been shown to stimulate food intake and may contribute to the adaptive response to energy deficiency or fasting. In the central nervous system, RXFP4 signaling interacts with hypothalamic neurocircuits that control feeding and metabolic balance. Emerging evidence also links RXFP4 activity to glucose metabolism and gut–brain axis communication. Overall, RXFP4 acts as a key metabolic and neuroendocrine receptor integrating nutritional, hormonal, and neural signals to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. For more information on RXFP4 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database.
RXFP4 (relaxin family peptide receptor 4) is a G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that primarily binds insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5), a member of the relaxin/insulin peptide family. Pharmacologically, RXFP4 couples predominantly to Gi/o proteins, resulting in inhibition of adenylate cyclase and reduced cyclic AMP (cAMP) production, although additional signaling pathways such as ERK1/2 activation have also been described. RXFP4 expression is mainly localized to the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the colon and rectum, but is also detected in the hypothalamus, pancreas, and adipose tissue, suggesting both peripheral and central roles. Functionally, the INSL5–RXFP4 system is implicated in the regulation of appetite, energy homeostasis, and gut motility. Activation of RXFP4 has been shown to stimulate food intake and may contribute to the adaptive response to energy deficiency or fasting. In the central nervous system, RXFP4 signaling interacts with hypothalamic neurocircuits that control feeding and metabolic balance. Emerging evidence also links RXFP4 activity to glucose metabolism and gut–brain axis communication. Overall, RXFP4 acts as a key metabolic and neuroendocrine receptor integrating nutritional, hormonal, and neural signals to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. For more information on RXFP4 pharmacology please refer to the IUPHAR database.
 pS354/pS359-RXFP4 (phospho-Relaxin Receptor 4...
pS354/pS359-RXFP4 (phospho-Relaxin Receptor 4... 
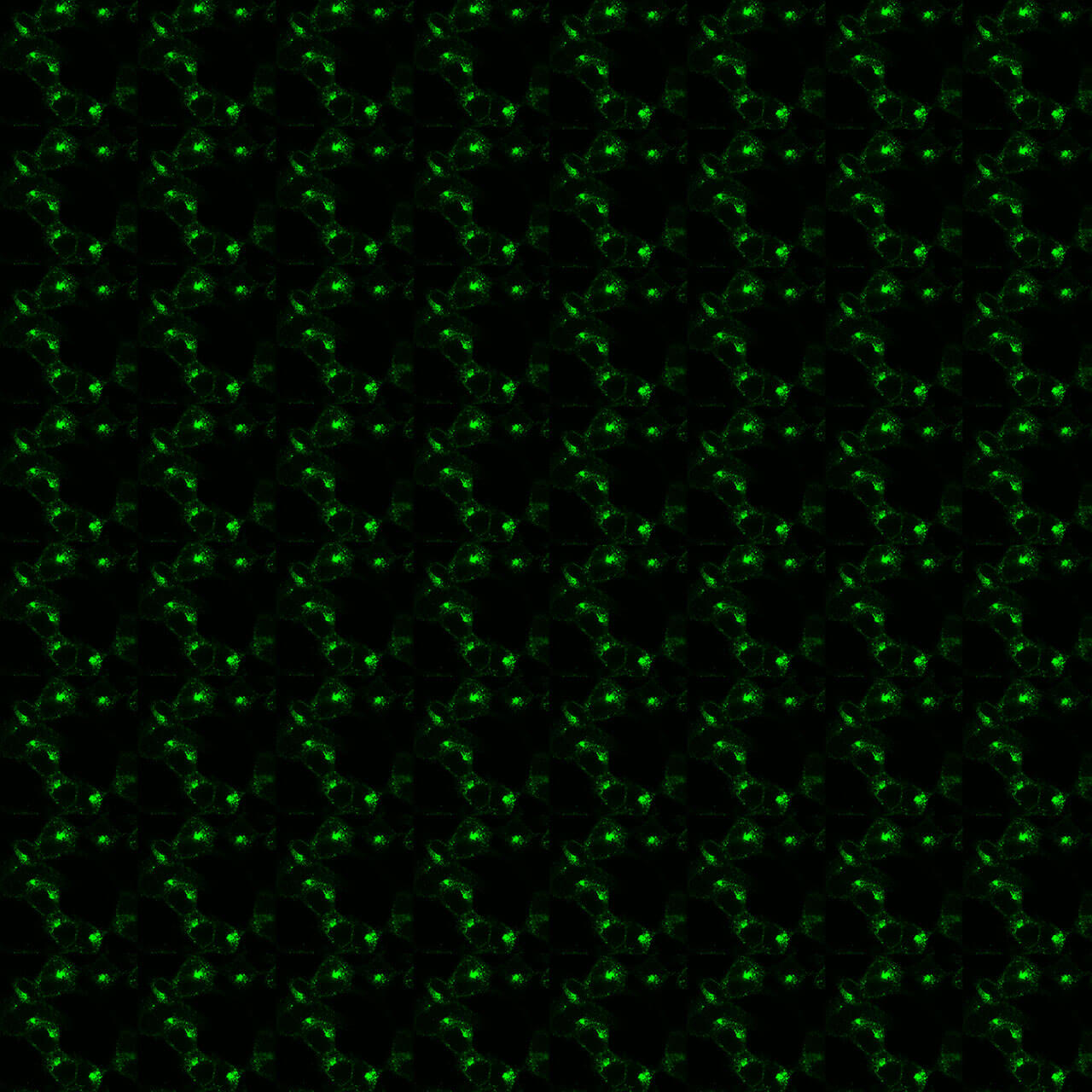
 RXFP4 (relaxin family peptide receptor 4) is a G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that primarily binds insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5), a member of the relaxin/insulin peptide family. Pharmacologically, RXFP4 couples predominantly to Gi/o proteins, resulting in inhibition of adenylate cyclase and reduced cyclic AMP (cAMP) production, although additional signaling pathways such as ERK1/2 activation have also been described. RXFP4 expression is mainly localized to the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the colon and rectum, but is also detected in the hypothalamus, pancreas, and adipose tissue, suggesting both peripheral and central roles. Functionally, the INSL5–RXFP4 system is implicated in the regulation of appetite, energy homeostasis, and gut motility. Activation of RXFP4 has been shown to stimulate food intake and may contribute to the adaptive response to energy deficiency or fasting. In the central nervous system, RXFP4 signaling interacts with hypothalamic neurocircuits that control feeding and metabolic balance. Emerging evidence also links RXFP4 activity to glucose metabolism and gut–brain axis communication. Overall, RXFP4 acts as a key metabolic and neuroendocrine receptor integrating nutritional, hormonal, and neural signals to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. For more information on RXFP4 pharmacology please refer to the
RXFP4 (relaxin family peptide receptor 4) is a G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) that primarily binds insulin-like peptide 5 (INSL5), a member of the relaxin/insulin peptide family. Pharmacologically, RXFP4 couples predominantly to Gi/o proteins, resulting in inhibition of adenylate cyclase and reduced cyclic AMP (cAMP) production, although additional signaling pathways such as ERK1/2 activation have also been described. RXFP4 expression is mainly localized to the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the colon and rectum, but is also detected in the hypothalamus, pancreas, and adipose tissue, suggesting both peripheral and central roles. Functionally, the INSL5–RXFP4 system is implicated in the regulation of appetite, energy homeostasis, and gut motility. Activation of RXFP4 has been shown to stimulate food intake and may contribute to the adaptive response to energy deficiency or fasting. In the central nervous system, RXFP4 signaling interacts with hypothalamic neurocircuits that control feeding and metabolic balance. Emerging evidence also links RXFP4 activity to glucose metabolism and gut–brain axis communication. Overall, RXFP4 acts as a key metabolic and neuroendocrine receptor integrating nutritional, hormonal, and neural signals to regulate appetite and energy expenditure. For more information on RXFP4 pharmacology please refer to the