Prices plus VAT plus shipping costs
Ready to ship today,
Delivery time appr. 5-8 days
- Order number: 7TM0319C
- Content: 100 µl
- Host: Rabbit
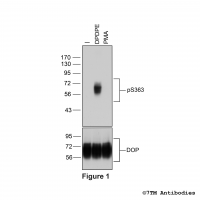
Serine375 (S375) is the primary phosphorylation site in a hierarchical phosphorylation cascade. The pS375-MOP antibody detects phosphorylation in response to high- and low-efficacy agonists but not after PKC activation. S375 phosphorylation is a key regulator of MOP desensitization, β-arrestin recruitment and internalization. The pS375-MOP antibody can by used for detection of the subcellular location of phosphorylated MOP by immunocytochemistry.
| Alternative Names | MOP, OPRM1, µ-Opioid Receptor, Mu Receptor |
| IUPHAR Target ID | 319 |
| UniProt ID | P35372 (human) P42866 (mouse) P33535 (rat) |
| Western Blot (WB) | 1:1000 |
| Immunocytochemistry (ICC) | 1:200 |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Immunogen | A synthetic phosphopeptide derived from human MOP around the phosphorylation site of Ser375 |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification | Antigen affinity chromatography |
| Storage buffer | Dulbecco's PBS, pH 7.4, with 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide |
| Storage conditions | short-term 4°C, long-term -20°C |
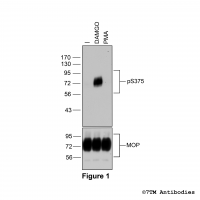
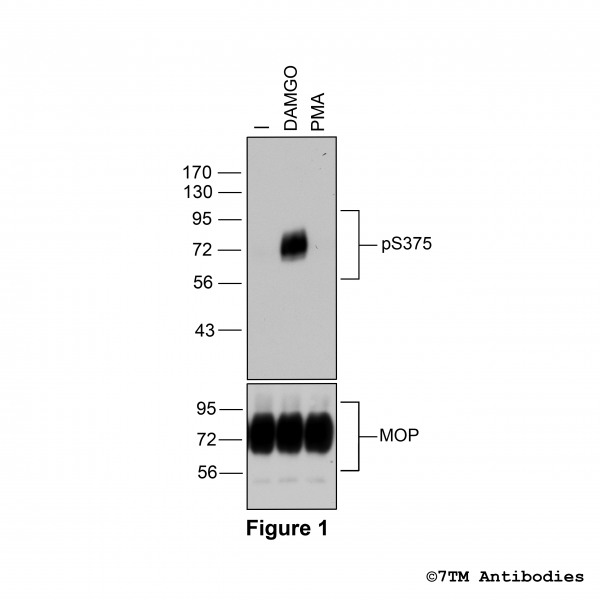
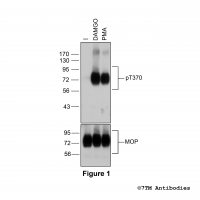
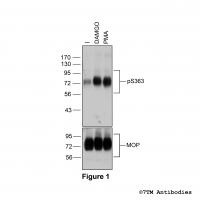
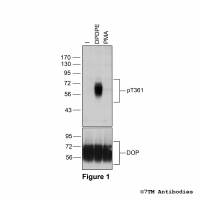
Figure 1. Agonist-induced Serine375 phosphorylation of the µ-Opioid Receptor. Upper panel, HEK293 cells stably expressing the µ-Opioid Receptor (MOP) were either not exposed or exposed to 10 μM DAMGO ([D-Ala2,N-MePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin) or 0.1 μM PMA (Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate) for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with the anti-pS375-MOP antibody (7TM0319C) at a dilution of 1:1000. Lower panel, blot was stripped and reprobed with the phosphorylation-independent anti-MOP antibody (7TM0319N-WB) at a dilution of 1:1000 to confirm equal loading of the gel.
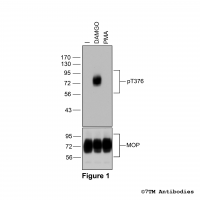
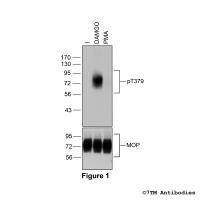
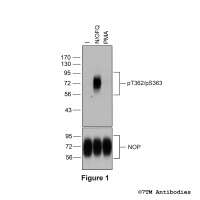
Figure 2. Analysis of dose-dependent µ-Opioid Receptor phosphorylation using a panel of phosphosite-specific antibodies. Upper four panels, HEK293 cells stably expressing the µ-Opioid Receptor (MOP) were either not exposed or exposed to increasing concentrations of DAMGO ([D-Ala2,N-MePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin) ranging from 1 nM to 1 μM for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with the anti-pT370-MOP antibody (7TM0319B) or anti-pS375-MOP antibody (7TM0319C) or anti-pT376-MOP antibody (7TM0319D) or anti-pT379-MOP antibody (7TM0319E) at a dilution of 1:1000. Lower panel, blot was stripped and reprobed with the phosphorylation-independent anti-MOP antibody (7TM0319N-WB) at a dilution of 1:1000 to confirm equal loading of the gel. Note, Serine375 is the primary site of phosphorylation.
Figure 3. Analysis of agonist-selective µ-Opioid Receptor phosphorylation using a panel of phosphosite-specific antibodies. Upper 4 panels, HEK293 cells stably expressing the µ-Opioid Receptor (MOP) were either not exposed or exposed to 10 µM morphine or 10 µM DAMGO ([D-Ala2,N-MePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin) for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted with the anti-pT370-MOP antibody (7TM0319B) or anti-pS375-MOP antibody (7TM0319C) or anti-pT376-MOP antibody (7TM0319D) or anti-pT379-MOP antibody (7TM0319E) at a dilution of 1:1000. Lower panel, blot was stripped and reprobed with the phosphorylation-independent anti-MOP antibody (7TM0319N-WB) at a dilution of 1:1000 to confirm equal loading of the gel. Note, DAMGO induces multisite phosphorylation. Morphine induces primarily the phosphorylation of Serine375.
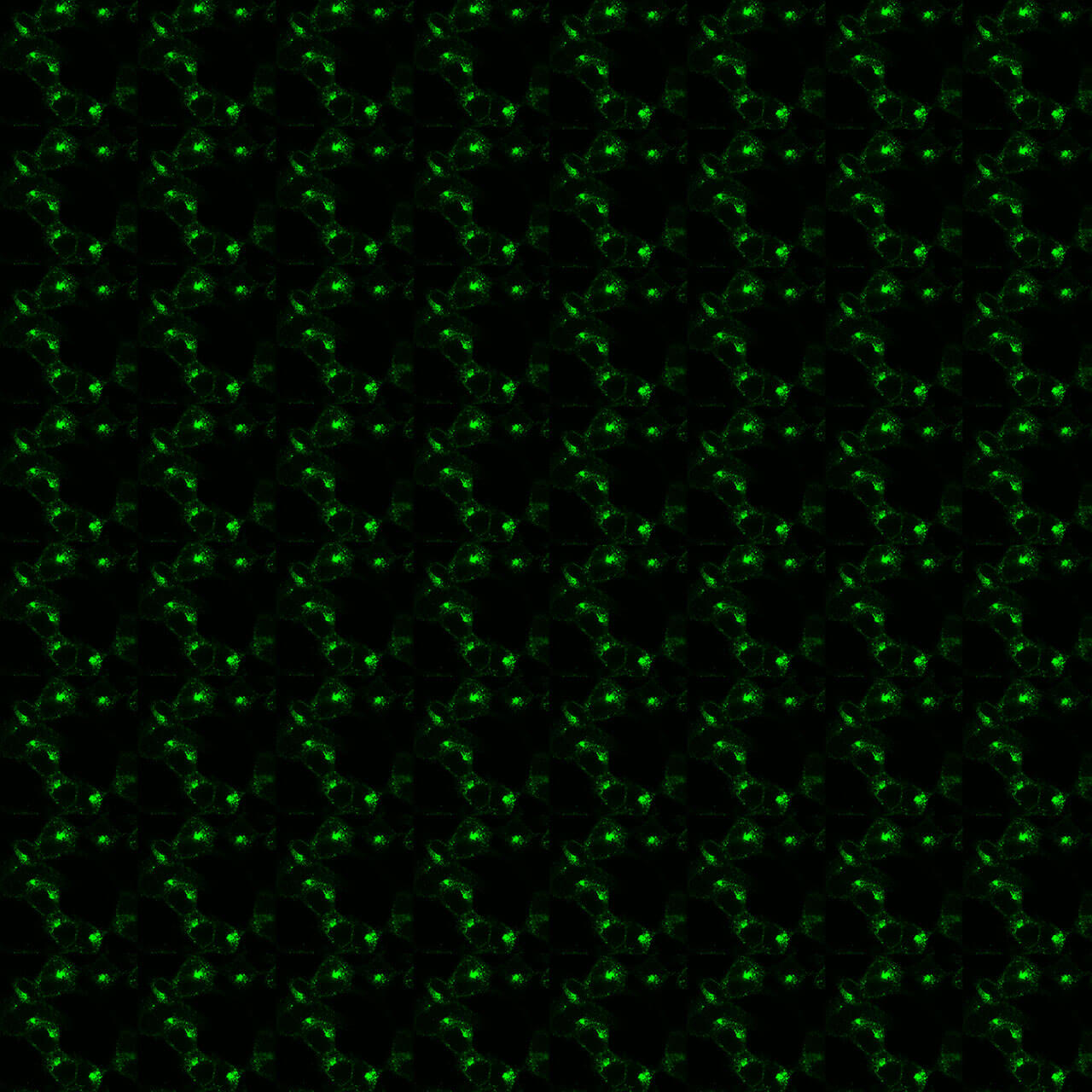
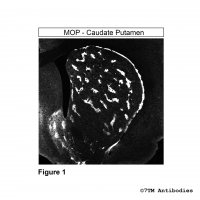
Figure 4. Immunocytochemical identification of Serine375 phosphorylation of the µ-Opioid Receptor. HEK293 cells stably expressing the µ-Opioid Receptor (MOP) were either not exposed or exposed to 10 μM DAMGO ([D-Ala2,N-MePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin) and immunocytochemically stained with the anti-pS375-MOP antibody (7TM0319C) at a dilution of 1:200. Note, Serine375-phosphorylated MOP receptors were not detectable in untreated cells (0 min). Serine375-phosphorylated MOP receptors were seen at the plasma membrane and perinuclear clusters of vesicles after 30 min of DAMGO treatment.
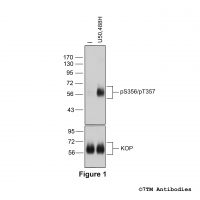
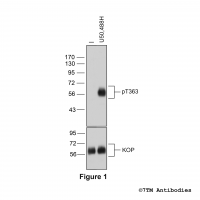
Figure 5. Agonist-induced Serine375 phosphorylation of the µ-Opioid Receptor in mouse brain in vivo. Upper panel, animals were either not treated or treated with the high-efficacy µ-agonist etonitazene (30 µg/kg, subcutaneous injection). After 30 minutes, brains were dissected, homogenated and immunoblotted using anti-pS375-MOP antibody (7TM0319C) at a dilution of 1:1000. Lower panel, blot was stripped and reprobed with the phosphorylation-independent anti-MOP antibody (7TM0319N-WB) at a dilution of 1:1000 to confirm equal loading of the gel. Note, absence of µ-Opioid Receptors in MOP-deficient mice (MOP-KO). Serine375-phosphorylated MOP receptors are only detected after agonist stimulation in wild-type mice (MOP-WT).
Kliewer A, Schmiedel F, Sianati S, Bailey A, Bateman JT, Levitt ES, Williams JT, Christie MJ, Schulz S. Phosphorylation-deficient G-protein-biased μ-opioid receptors improve analgesia and diminish tolerance but worsen opioid side effects. Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 21;10(1):367. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08162-1. PubMed PMID: 30664663; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6341117.
Miess E, Gondin AB, Yousuf A, Steinborn R, Mösslein N, Yang Y, Göldner M, Ruland JG, Bünemann M, Krasel C, Christie MJ, Halls ML, Schulz S, Canals M. Multisite phosphorylation is required for sustained interaction with GRKs and arrestins during rapid μ-opioid receptor desensitization. Sci Signal. 2018 Jul 17;11(539). pii: eaas9609. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aas9609. PubMed PMID: 30018083.
Yousuf A, Miess E, Sianati S, Du YP, Schulz S, Christie MJ. Role of Phosphorylation Sites in Desensitization of µ-Opioid Receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;88(4):825-35. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.098244. Epub 2015 May 12. PubMed PMID: 25969388.
Radoux-Mergault A, Oberhauser L, Aureli S, Gervasio FL, Stoeber M.Subcellular location defines GPCR signal transduction. Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 21;9(16):eadf6059. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf6059. Epub 2023 Apr 19. PMID: 37075112; PMCID: PMC10115417.
Just S, Illing S, Trester-Zedlitz M, Lau EK, Kotowski SJ, Miess E, Mann A, Doll C, Trinidad JC, Burlingame AL, von Zastrow M, Schulz S. Differentiation of opioid drug effects by hierarchical multi-site phosphorylation. Mol Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;83(3):633-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.082875. Epub 2012 Dec 13. PubMed PMID: 23239825; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3583494.
Doll C, Pöll F, Peuker K, Loktev A, Glück L, Schulz S. Deciphering µ-opioid receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in HEK293 cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;167(6):1259-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02080.x. PubMed PMID: 22725608; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3504992.
Grecksch G, Just S, Pierstorff C, Imhof AK, Glück L, Doll C, Lupp A, Becker A, Koch T, Stumm R, Höllt V, Schulz S. Analgesic tolerance to high-efficacy agonists but not to morphine is diminished in phosphorylation-deficient S375A μ-opioid receptor knock-in mice. J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 28;31(39):13890-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2304-11.2011. PubMed PMID: 21957251; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC6633166.
Doll C, Konietzko J, Pöll F, Koch T, Höllt V, Schulz S. Agonist-selective patterns of µ-opioid receptor phosphorylation revealed by phosphosite-specific antibodies. Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2):298-307. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01382.x. PubMed PMID: 21449911; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3174411.
Dasgupta P, Mann A, Polgar WE, Reinscheid RK, Zaveri NT, Schulz S. Attenuated G protein signaling and minimal receptor phosphorylation as a biochemical signature of low side-effect opioid analgesics. Sci Rep. 2022 May 3;12(1):7154. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11189-6. PMID: 35504962; PMCID: PMC9065038.
Celik MÖ, Seitz V, Yergöz F, Dembla S, Blum NK, Schulz S, Stein C. Modulation of G-protein activation, calcium currents and opioid receptor phosphorylation by the pH-dependent antinociceptive agonist NFEPP. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 May 12;16:1171855. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1171855. PMID: 37251645; PMCID: PMC10213447.
Underwood O, Fritzwanker S, Glenn J, Blum NK, Batista-Gondin A, Drube J, Hoffmann C, Briddon SJ, Schulz S, Canals M. Key phosphorylation sites for robust β-arrestin2 binding at the MOR revisited. Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 2;7(1):933. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06571-1. PMID: 39095612; PMCID: PMC11297201.